Cardiac Procedures
Invasive Cardiac Investigations and Procedures
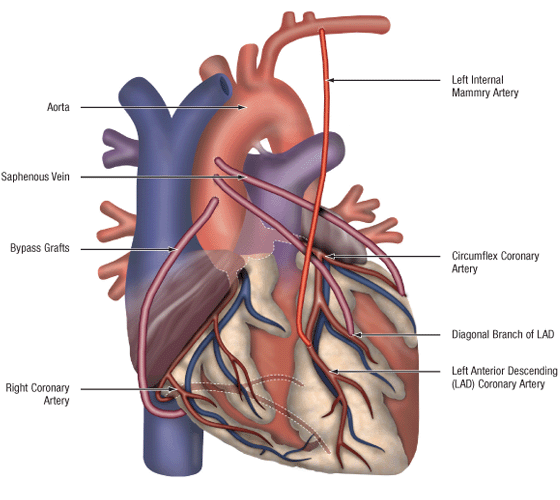
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical technique whereby veins are taken from the legs and an artery is taken from the chest wall. They are used to bridge or bypass narrowed areas in coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart. Newer procedures include total arterial revascularization: where arteries from the right and left chest wall and from the forearm are used to create all the bypass grafts, and the MID-CAB procedure where bypass of single vessel LAD disease is carried out on the beating heart through a small incision in the anterior chest wall. In some cases, coronary bypass may even be carried out off pump (OP-CABG) to avoid stopping the heart, so called beating heart bypass surgery. These newer procedures have specific indications, which can be discussed with your cardiac surgeon.
CABG is very good therapy for angina particularly when medications or angioplasty cannot control angina. The surgery may also be indicated where cardiac testing shows a high risk for extensive heart damage to occur if the patient were to suffer a heart attack.
The operation usually takes about 4 hours and the patient is usually in hospital about
5-7 days. The patient usually resumes normal activities by around 2 months after the surgery and may return to work in 3-4 months. The risk of bypass surgery includes an approximate 1% risk of death and 5% risk of heart attack, stroke or wound infection.
|